Nedinoschiza khuathalinhae Long, 2022
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5116.4.5 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:18824DD4-FED1-4242-BD50-5FE47650CBBF |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7509860 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/038A0336-8F22-FF90-FF1C-FF38FF5FDFF3 |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Nedinoschiza khuathalinhae Long |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Nedinoschiza khuathalinhae Long , sp. nov.
( Figs 35–49 View FIGURE 35 View FIGURES 36–48 View FIGURES 49 )
Material examined. Holotype, ♀, “Bracn. 1485 ” ( IEBR), NE Vietnam: Tuyen Quang, Na Hang NP, Son Phu , forest, MT, 22°17’32’’N 105°28’19’’E, 570 m, 15.vii.2017, KD Long GoogleMaps . Paratypes 5 ♀, “Bracn. 1087 ” ( IEBR), NC Vietnam, Ha Tinh, Huong Son , forest, 18°22’ N 105°13’ E, 450 m, April 7–13 1998. Malaise, AMNH, K. Long; “Bracn. 1088 ” ( AMNH), GoogleMaps ibid., but 600 m, April 15–21, 1998, Malaise AMNH, K. Long; “Bracn. 1564 ”, “Bracn. 1565 ” ( IEBR), “Bracn. 1566 ” ( RMNH), GoogleMaps NE Vietnam: Tuyen Quang, Na Hang NP, Son Phu, forest, MT, 22°17’32’’N 105°28’19’’E, 570 m, 25.ix.2017, KD Long GoogleMaps ; 1 ♂, “Bracn. 524 ” ( IEBR), NC Vietnam, Ha Tinh, Huong Son , forest, 18°22’ N 105°13’E, 300 m, 28.iv.1998, sweep, K. Long GoogleMaps .
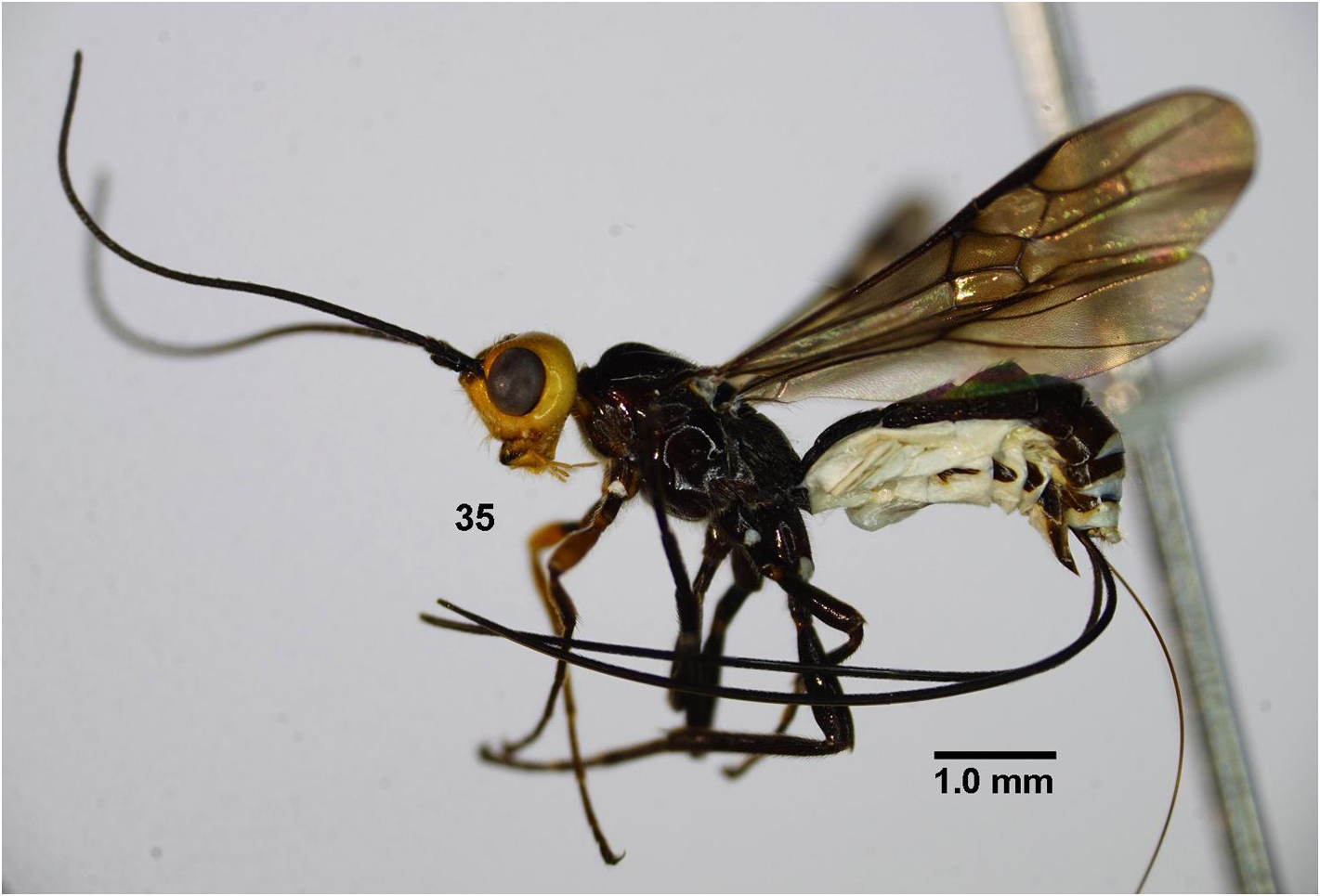
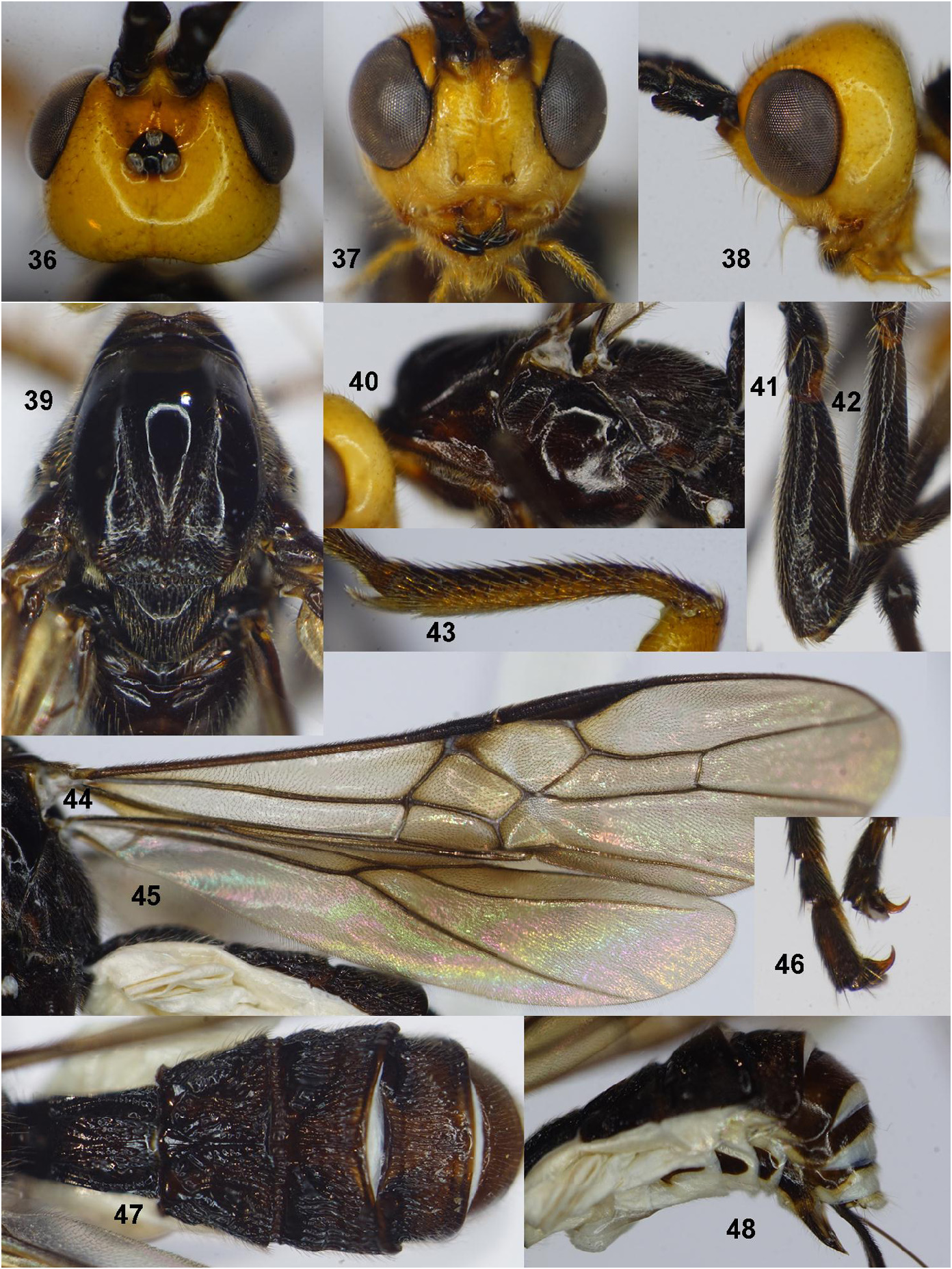
Description. Holotype, female, length of body 6.7 mm, fore wing 6.5 mm, antenna 5.6 mm, ovipositor sheath 7.7 mm ( Fig. 35 View FIGURE 35 ).
Head. Antenna with 39 antennomeres; length of first flagellomere 1.1 × second (9: 8); first and second flagellomere 2.25 and 2.0 × as long as wide respectively; head 1.2 and 1.3 × as wide as long in anterior (frontal) and dorsal view respectively; clypeus separated from face with distinct transverse carina; face as wide as long, with wide groove between antennal sockets, sparsely setose, smooth medially, punctate laterally ( Fig.37 View FIGURES 36–48 ); in frontal view, eye length 1.9 × as long as its transverse width (28: 15); height of clypeus: inter tentorial distance: tentorial ocular distance = 5: 9: 9; distance between tentorial pits as long as distance from tentorial pit to eye margin ( Fig. 37 View FIGURES 36–48 ); malar space 0.9 × basal width of mandible (10: 11); in lateral view, transverse width of eye 1.25 × as long as temple (20: 16) ( Fig. 38 View FIGURES 36–48 ); in dorsal view length of eye 1.3 × as long as temple (21: 16), sparsely setose, not emarginated beyond antennal sockets ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 36–48 ); POL: OD: OOL = 4: 4: 13; frons distinctly depressed laterally, with median carina, smooth; vertex and temple smooth, with fine sparse punctures and setae.
Mesosoma. Mesosoma 1.7 × as long as high (100: 60) ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 36–48 ); mesoscutum smooth, setose, glabrous laterally; notauli distinct, shallow; scutellar sulcus narrow, punctate ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 36–48 ); scutellum smooth, setose; mesopleuron smooth medially, sparsely punctate and setose posteriorly ( Fig. 40 View FIGURES 36–48 ); metapleuron sparsely punctate and setose; median area of metanotum without midlongitudinal carina anteriorly; propodeum almost smooth, sparsely punctate and setose.
Wings. Fore wing ( Fig. 44 View FIGURES 36–48 ): length of pterostigma 4.0 × its width; angle between vein C+SC+R and 1-RS about 70°; vein 1-RS+M curved basally; ratio of length of veins r: 2-RS: 3-RS: SR1 = 9: 18: 37: 61 and 2-RS: 3-RS: r-m = 19: 37: 11; vein 1cu-a slightly postfurcal; second submarginal cell parallel sided, basal length 5.0 × its apical width ( Fig. 44 View FIGURES 36–48 ). Hind wing ( Fig. 45 View FIGURES 36–48 ): apex of vein C-SC+R1 with one straight hamulus; vein 2-SC+R longitudinal; vein SR slightly curved subbasally, narrowed apically ( Fig. 45 View FIGURES 36–48 ); vein 1r-m 1.25 × 2-SC+R; apex of vein SC+R1 with three curved hamuli.
Legs. Ratio of lengths of fore femur: tibia: basitarsus: hind tarsus = 32: 30: 23: 66; fore tibia: fore tarsus (30: 66); fore tibia with stout setae ( Fig. 43 View FIGURES 36–48 ); middle femur ( Fig. 42 View FIGURES 36–48 ) and hind femur robust ( Fig. 41 View FIGURES 36–48 ); ratio of lengths of hind femur: tibia: basitarsus: hind tarsus = 52: 91: 31: 85; hind femur, tibia, basitarsus 3.25, 10.1 and 5.2 × as long as wide respectively; outer and inner hind tibial spurs 0.25 × and 0.35 × as long as hind basitarsus; hind coxa finely and sparsely punctate, with long setae; tarsal claw simple, without pointed basal lobe ( Fig. 46 View FIGURES 36–48 ).
Metasoma. First metasomal tergite 1.3 × as long as wide apically (40: 30), distinctly rugose with a midlongitudinal carina and a pair of lateral smooth longitudinal groove ( Fig. 47 View FIGURES 36–48 ); second metasomal tergite rugose, 1.5 × as long as third tergite (30: 20), and 1.3 × as wide (basally) as long (40: 30); longitudinally striate area, with a pair of smooth sublateral areas and lateral shallow, crenulated grooves, midbasal area of second tergite 0.4 × median length of the tergite, connected with second metasomal suture by longitudinal carina in 0.6 apical of the tergite (18: 30); lateral sides of midbasal area crenulated ( Fig. 47 View FIGURES 36–48 ); second metasomal suture wide, crenulate; divergent grooves of second tergite wide and crenulate; third-fourth tergites rugo-striate ( Fig. 47 View FIGURES 36–48 ); fifth-sixth metasomal tergites smooth, with sparse setae and fine punctures; hypopygium acute apically ( Fig. 48 View FIGURES 36–48 ); ovipositor sheath setose, 1.2 × as long as fore wing; ovipositor very thin, with dorsal nodus and ventral serrations.
Colour. Body black; head yellow ( Fig. 35 View FIGURE 35 ); stemmaticum black ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 36–48 ); antenna black; fore coxa and tibia yellow; fore femur yellow, except base black; fore trochanters and trochantellus black; middle and hind legs black; wings black; ovipositor sheath dark brown; ovipositor brown.
Variation. Females: length of body 5.3–9.0 mm; fore wing 4.6–8.4 mm; antenna with 37–41 antennomeres.
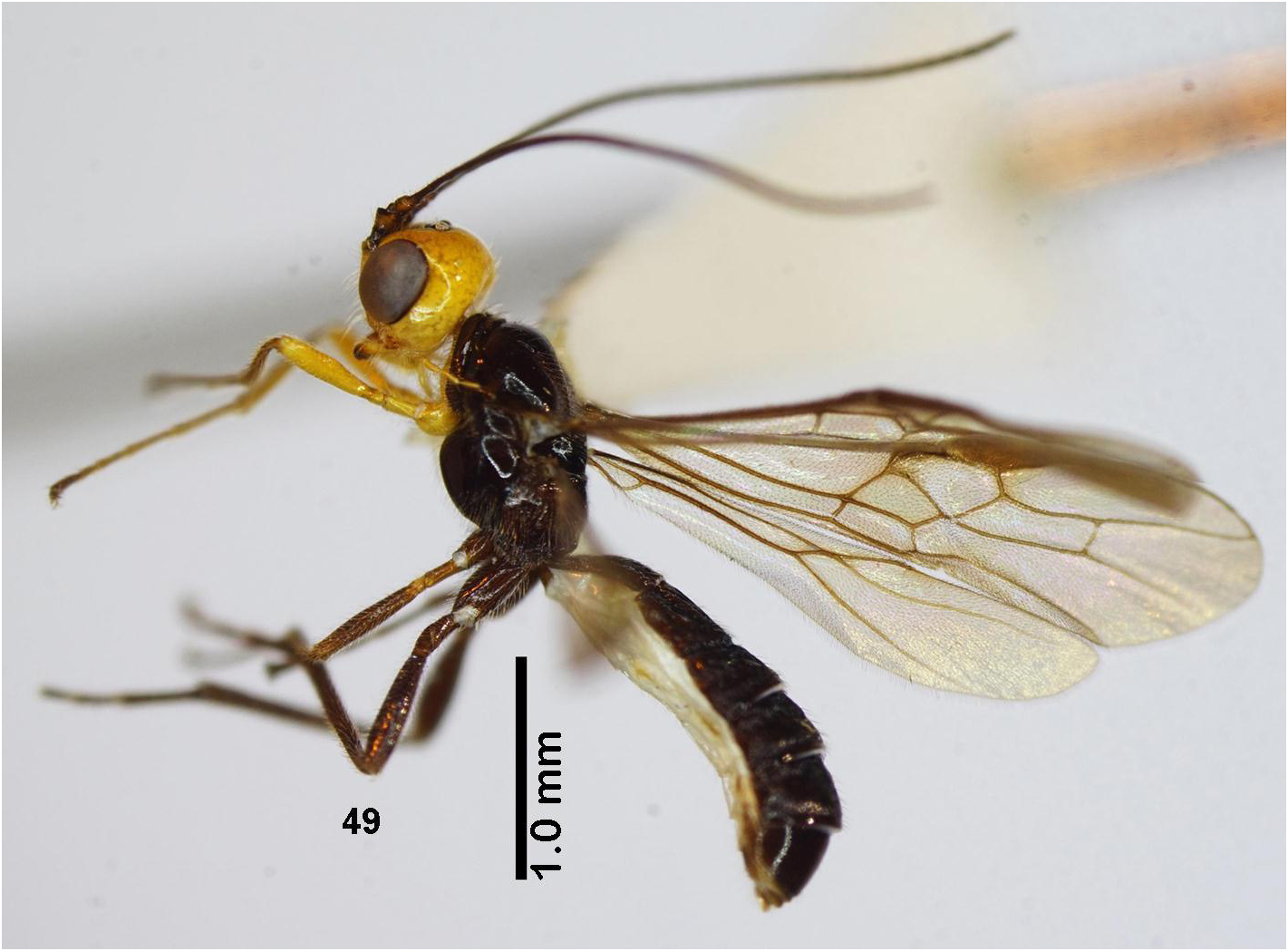
Male. Length of body 4.1 mm, fore wing 4.1 mm, antenna 3.5 mm; antenna with 30 antennomeres ( Fig. 49 View FIGURES 49 ).
Distribution. NE Vietnam ( Tuyen Quang); NC Vietnam ( Ha Tinh).
Biology. Unknown.
Etymology. The new species is named after the granddaughter of the second author, Khuat Ha Linh.
Notes. Nedinoschiza khuathalinhae sp. nov. is similar to Nedinoschiza pinguis Papp , from China in having the longitudinally striated midbasal area of second metasomal tergite and sculptured third metasomal tergite, but differs from N. pinguis by the following characters: 1) Length of eye 1.3 × as long as temple in dorsal view ( Fig. 36 View FIGURES 36–48 ) [ vs 0.8 × in N. pinguis , cf. Fig. 4C View FIGURES 2–11 in Ranjith & Priyadarsanan (2021)]; 2) Midbasal area of second metasomal tergite 0.4 × second tergite length ( Fig. 47 View FIGURES 36–48 ) [ vs 0.75 × in N. pinguis , cf. Fig. 5A View FIGURES 2–11 in Ranjith & Priyadarsanan (2021)]; and 3) Pronotum and mesoscutum black ( Fig. 39 View FIGURES 36–48 ) [ vs yellow in N. pinguis , cf. Figs 4D, E View FIGURES 2–11 in Ranjith & Priyadarsanan (2021)].
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |