Erythropompilus macroplacoideus Wu & Ma, 2023
|
publication ID |
https://doi.org/10.11646/zootaxa.5244.2.4 |
|
publication LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:pub:B89B5171-3D4D-4FDD-8CCF-94DCE8A56EAE |
|
DOI |
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7670776 |
|
persistent identifier |
https://treatment.plazi.org/id/1DF79C9F-7F8D-41C7-BDAF-0253B503357F |
|
taxon LSID |
lsid:zoobank.org:act:1DF79C9F-7F8D-41C7-BDAF-0253B503357F |
|
treatment provided by |
Plazi |
|
scientific name |
Erythropompilus macroplacoideus Wu & Ma |
| status |
sp. nov. |
Erythropompilus macroplacoideus Wu & Ma , sp. nov.
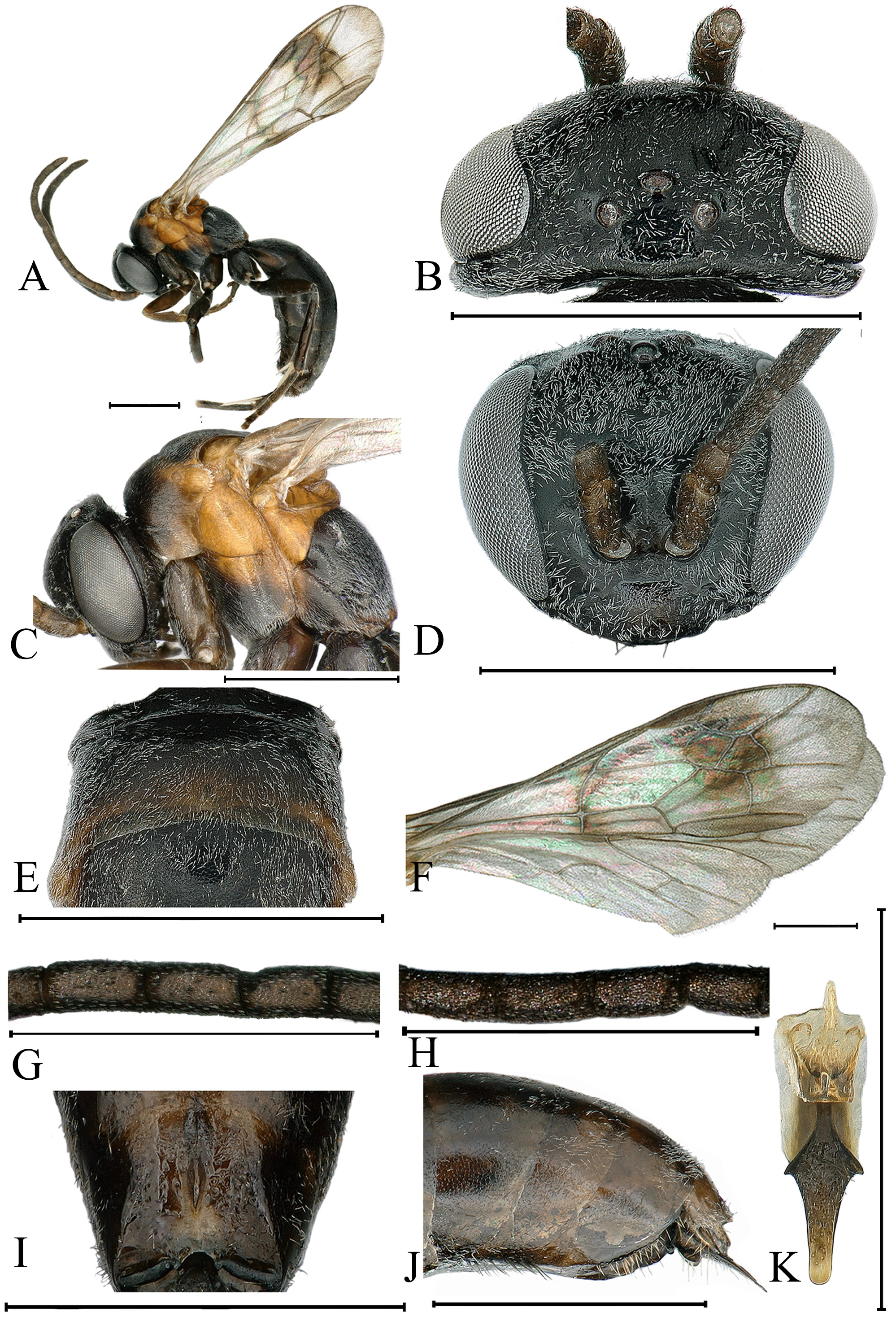
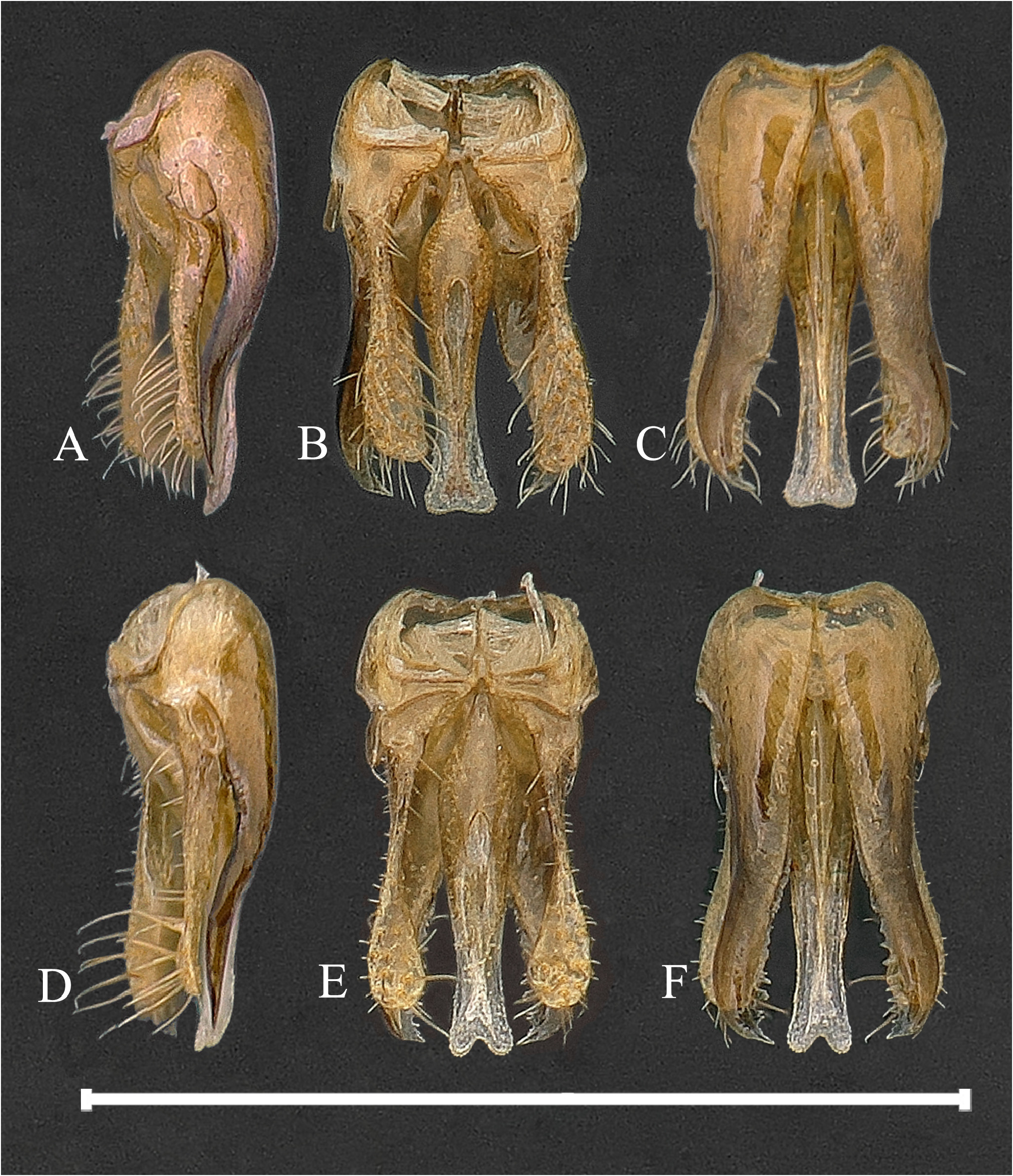
Figs 2 View FIGURE 2 , 3 View FIGURE 3 , 4 View FIGURE 4 (D–F)
urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:
Material examined. Holotype: CHINA, Yunnan, Jinghong, Menghai, Bulang Mountain , ♀, 21°45′N 100°26′E, 1683 m, Malaise trap, 17.V–25.VI.2021, coll. Yong-sheng Pu (YNAU) GoogleMaps . Paratypes: CHINA, Yunnan, 1♀ 1♁, same locality as holotype, 17.V–21.VI.2018, coll. Ling Zhao (YNAU) GoogleMaps .
Diagnosis. The new species is similar to E. taiwanensis Pitts & Shimizu, 2021 in having the following characteristics: frons strongly convex in profile ( Figs 2C View FIGURE 2 , 3C View FIGURE 3 ); clypeus less than LID ( Figs 2D View FIGURE 2 , 3D View FIGURE 3 ); ratio of POD/ OOD larger than 0.85; gena, in dorsal view, thickened, roundly receding posteriorly ( Figs 2B View FIGURE 2 , 3B View FIGURE 3 ); mid and hind femora without small spines set in pits apicodorsally; but markedly differs by the characters given in the Table 2. View TABLE 2
Description. Female. (Measurements of the holotype are given in parentheses.) Length: Body 6.0–6.5 (6.5) mm; forewing 5.3–5.6 (5.6) mm. Body black, mandible red-brown at apical 1/3, mandible with 2 brown long setae on basal 2/5 ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ), the following brown: beneath of scape, apical 1/6 of fore coxa and femur ventrally, fore tibia ventrally; Mesosoma orange-red, expect for collar, anterior margin of pronotum and lower 1/7 of mesopleuron, sometimes propodeum black ( Figs 2A, 2J View FIGURE 2 ).
Head: Mandible with one inner tooth, clypeus slightly convex in lateral view, anterior margin nearly straight ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ). In frontal view, head 1.25 × as broad as long; vertex distinctly convex between eye tops, frontal line fine and inconspicuous; MID large, 0.63–0.64 (0.64) as broad as TFD, UID: MID: LID = 8.5: 10: 7.5–8 (8); clypeus 2.3 × as broad as long, clypeus width less than LID ( Fig. 2D View FIGURE 2 ). In dorsal view, ocellar area with several sparse punctures, ocelli in obtuse triangle, POD: OOD = 1: 0.9; antennocular line, in dorsal view, distinctly inclined from antennal base toward eye ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ); F1 4.2 × as long as thick, 0.68 × as long as UID; length ratios of scape, pedicel, F1–F3 = 12: 5: 18: 16: 15. Flagellomeres with placoid sensilla on inner and external surfaces, external sensilla more than 3/4 each flagellomere, internal F1–F6 less than half of each flagellomere, apical 4 segments less than half of each flagellomere, gena slightly thickened, 0.3 × eye width ( Fig. 2C View FIGURE 2 ).
Mesosoma: Lateral margin of pronotal dorsum, in dorsal view, anteriorly slightly narrower than posterior area, pronotum posterior margin slightly arcuate ( Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 ), pronotum conspicuously shorter than mesoscutum; in dorsal view, mesoscutum flat, slightly inclined towards posteriorly, parapsidal sulcus reaching nearly 5/6 of mesoscutum; scutellum disc raised, but not convex above level of mesoscutum; metanotum posterior margin extending at middle and covering partly postnotum, postnotum nearly 1/10 as long as metanotum, depressed medially and narrower than laterally ( Fig. 2G View FIGURE 2 ). propodeum, in dorsal view, parallel-sided at anterior half, narrowing at posterior half, in lateral view, gently convex, posterior slope at apical 1/3; propodeal enclosure irregularly rugose, and with two longitudinal carinae medially.
Wing: Pterostigma long, about 5 × as long as 2r-rs ( Fig. 2F View FIGURE 2 ); marginal cell removed from wing tip by 0.57 (0.5) × its own length; SMC2: SMC3 = 1: 1.6 on vein M, 1: 0.5 on vein RS; SMC2 broad on vein RS, equal to its length on vein M, receiving crossvein 1m-cu at basal 1/2; SMC3 narrowed on vein RS by 0.3 × its length on vein M, receiving crossvein 2m-cu at basal 0.6, removed from outer wing margin by 1.7 × its own length, crossvein cu-a originating basally to fork of vein M+CuA; HW crossvein cu-a arcute, originating much basal to fork of vein M+CuA.
Legs: Mid femur without small spines set in pits apicodorsally, mid tibia dorsally with 4 long brown spines externally and without spines internally, mid tibia ventrally with 2 small brown spines externally and 1 internally respectively; hind tibia dorsally with 6–7 long brown spines externally and 3–5 long brown spines internally, hind tibia ventrally with 1–3 small brown spines externally and 2 small brown spines internally. Longer spur of hind tibia 0.68 × hind tarsomere 1.
Male. Differs from female as follows: body length 4.0 mm; forewing 3.8 mm; antenna, clypeus, labrum, mandible basally, all legs and metasoma dark rufous; scape and pedicel ventrally, femur and tibia of fore leg pale brown; pronotum largely, mesoscutum and propodeum black ( Fig. 3A View FIGURE 3 ).
Head: In frontal view, head 1.19 × as broad as long ( Fig. 3D View FIGURE 3 ); MID large than female, 0.66 as broad as TFD, UID: MID: LID = 9: 10: 8.3; clypeus 2.5 × as broad as long, F1 2.7 × as long as thick, 0.44 × as long as UID; length ratio of scape, pedicel, F I–III = 10: 4: 12: 12: 13 ( Fig. 3H View FIGURE 3 ), gena narrow, 0.25 × eye width ( Fig. 3C View FIGURE 3 ).
Mesosoma: Notaulus of mesoscutum fine and short anteriorly and medially.
Wing: FW inner fasciae light, narrower than that in female, marginal cell removed from wing tip by 0.38 × its own length; SMC2: SMC3 = 1: 1.8 on vein M.
Legs: Mid tibia dorsally with 3 short brown spines externally, mid tibia ventrally without spine internally; hind tibia dorsally with 3 short brown spines externally and without spine internally.
Metasoma: Side of S4 and S5, each with tuft of sparse, erect and black bristles ( Fig. 3J View FIGURE 3 ); S6 flat in basal 1/4, with oblique declivity in apical 3/4, posterior margin with inverted V-shaped edge ( Fig. 3J View FIGURE 3 ); S6 with blade-like longitudinal keel far from posterior margin ( Fig. 3J View FIGURE 3 ).
SGP and genitalia: Exposed portion of SGP narrowing apically, subbasally widest, rounded and translucent apically ( Fig. 3K View FIGURE 3 ); in lateral view, SGP flat, with clearly triangular-shape ridge basally, and some sparse short setae in basal 2/3 ( Fig. 3J View FIGURE 3 ). Paramere very short, peg-like ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ); volsella narrow at basal 1/2, gradually broadened towards apex, rounded apically, and with several long setae at apical 1/3 ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ); parapenial lobe slightly extending apex of volsella, inner margin entirely with fine and irregular serrate ( Fig. 4F View FIGURE 4 ); aedeagus slightly longer than parapenial lobe, mostly parallel-sided, apical margin conspicuously concave medially ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ).
Distribution. China ( Yunnan).
Sex association. Not only were all the female and male specimens collected from the same Malaise trap, but they also have the same pattern and the following common characteristics: ratio of POD: OOD; clypeus <LID; in dorsal view, gena slightly thicken; frons strongly convex; and body color.
Etymology. The name macroplacoideus originates from the Greek word " mac "(=long, large) and " placoideus " (= placoid), referring to the flagellomeres of male with huge placoid sensilla.
TABLE 2. Structural differences between E. macroplacoideus Wu & Ma, sp. nov. and E. taiwanensis Pitts & Shimizu, 2021, female and male.
| E. macroplacoideus Wu & Ma , sp. nov. | E. taiwanensis Pitts & Shimizu, 2021 |
|---|---|
| a Mesosoma partly orange-red ( Fig. 2B View FIGURE 2 ). ( ♀, ♁) | Mesosoma entirely black (female) or dark rufous. (♁) |
| b Lateral margin of pronotal dorsum, in dorsal view, | Lateral margin of pronotal dorsum, in dorsal view, not |
| slightly narrowing anteriorly ( Fig. 2E View FIGURE 2 ). ( ♀) | narrowing anteriorly. ( ♀) |
| c F1/ UID about 0.7 ( ♀), F1 / UID <0.5. (♁) d Placoid sensilla large, more than 3/4 of each | F1/ UID about 0.8 ( ♀), F1 /UID> 0.5. (♁) Placoid sensilla small, much shorter than 1/2 of each |
| flagellomere ( Fig. 3H View FIGURE 3 ). (♁) | flagellomere. (♁) |
| e Paramere very short ( Fig. 4D View FIGURE 4 ). (♁) | Paramere long. (♁) |
| f Aedeagus extending beyond apex of parapenial lobe, | Aedeagus not extending beyond apex of parapenial lobe, |
| and apex conspicuously concave medially ( Fig. 4E View FIGURE 4 ). (♁) | and apical margin not emarginated medially. (♁) |
No known copyright restrictions apply. See Agosti, D., Egloff, W., 2009. Taxonomic information exchange and copyright: the Plazi approach. BMC Research Notes 2009, 2:53 for further explanation.
|
Kingdom |
|
|
Phylum |
|
|
Class |
|
|
Order |
|
|
Family |
|
|
Genus |